The process of conducting a procurement audit helps to ensure that suppliers are actively following contracts and accurately reporting their internal operations. As a dynamic field that can rapidly shift with new emerging technologies, developing regulations, and fundamental changes, businesses must stay up-to-date with modern audit strategies.
Over the past decade, we’ve seen numerous shifts in this field and their international web of impacts radically altered the modern supply chain. Each major trend in procurement auditing helps to refine the technologies, strategies, and common methods that auditors use in the sector.
Understanding the developing trends that are occurring in 2024 will allow businesses to stay ahead of the curve and excel when creating a sustainable, effective, and long-lasting supply chain.
Digital Transformation in Procurement Audit
Digital transformation of the supply chain is quite possibly the most impactful trend actively shaping procurement auditing. New technologies have begun to emerge, providing suppliers and organisations alike with new opportunities to improve operational efficiency.
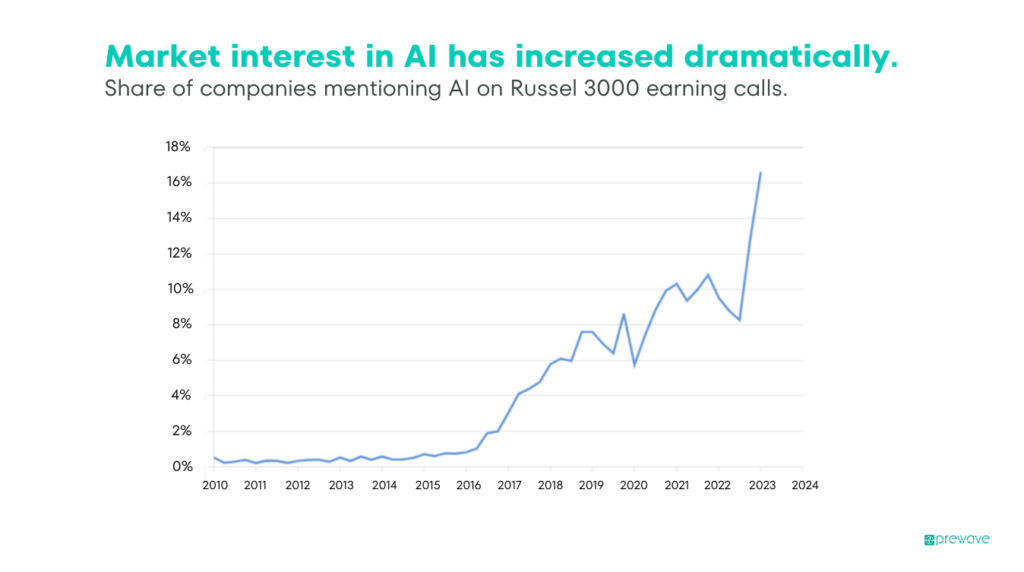
Even within the last three years, the rapid introduction and expansion of the capabilities of artificial intelligence (AI) technologies have completely altered common practice in procurement auditing. As a field that reflects the complexity and technological transformation of the various suppliers it is connected to, this form of auditing is always ahead of major industry trends.
AI technology allows businesses to process millions of individual points of data in a fraction of the time that it would take an auditor. This speed allows auditing teams to produce more comprehensive reports in much less time. AI is already making waves in procurement auditing, impacting everything from contract analysis and management to supplier risk observation.
By leveraging historical supplier data, market trends, country profiles, and other external factors, auditors can produce a more accurate analysis of potential risks.
Another form of digital transformation that goes hand-in-hand with AI is the development of more precise data analytics tools. AI can often provide the power needed to create comprehensive software that can monitor, observe, and predict risk in real-time. Applying this at scale can create a complex web of understanding, giving businesses full insight into the suppliers they use.
Auditors can leverage these emerging technologies to gain deeper insights into their suppliers. Digital transformation has recently seen a dramatic increase in utility in procurement auditing, with the increasing investment into data and AI only serving to accelerate this trend in the future.
Blockchain and Supply Chain Transparency
Blockchain technology acts as an ongoing ledger of information. Once data is recorded to a block, it is impossible to modify or remove. With that in mind, integrating blockchain technologies into procurement audit helps to guarantee its authenticity, integrity, and transparency.
Blockchain offers numerous ways of enhancing the validity of procurement audits:
- Supply Chain Tracking – Logging every step of movement across the supply chain, including the source and transport of raw materials, ensures that no one can hide information in the process. Instead of trusting the reporting structures of a company, businesses can rest assured that all movements are valid. This tracking boosts transparency and prevents fraudulent materials and shipments from entering the supply chain.
- Enhanced Visibility – The blockchain is a public ledger, meaning that all vendors will have access to a real-time method of tracking their materials and shipments. Real-time visibility enhances transparency in the system and provides a more accurate ledger of information for audits to use.
- Reduced Data Manipulation – As blockchain systems produce an immutable ledger, it’s impossible to change the status of reports after they are submitted. This instantly eliminates the possibility of data manipulation, enhancing the auditing process and increasing levels of reporting honesty in the field.
Blockchain is another emerging technology that’s making radical changes to procurement audits, enhancing their efficacy while removing doubt and enhancing transparency.
Risk Management and Predictive Analytics
Over the past few decades, the primary method of risk management was highly reactive. By planning out the actionable steps that a company would take if a critical event were to occur, they can quickly mobilise a response.
While reactive risk management allowed businesses to respond to threats and overcome them, it did very little to actually decrease the likelihood of these events from occurring. Especially with the rising availability of powerful AI and data-first tools, this trend is shifting.
Businesses are increasingly using predictive analytics to identify potential threats before they occur, switching to a proactive strategy that nullifies risk as early as possible. The movement toward proactive risk management is enabled entirely by predictive analytics.
Predictive analytics allow auditors to more rapidly find potential risks, like regulatory shifts impinging on trade, contractual breaches impacting compliance, and patterns of fraud.
By analysing millions of data points, predictive analytics tools can identify risks and suggest mitigating strategies ahead of time. For example, a business may locate a high level of risk in one of their suppliers. By phasing out that supplier over time and replacing them with more reliable sources, the organisation avoids all potential consequences of working with that supplier.
Preventative measures allow businesses to take control ahead of time.
Regulatory Compliance in a Global Context
For many businesses, a standard supply chain is a webbed nexus that stretches across the globe and moves through several political territories. In this international context, shifts in local and governmental policy can create disruptions or completely derail supply chain transits.
Understanding that every supply chain exists in this global context is vital to sustained success. While larger compliance frameworks like the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) are highly standardised at this point, emerging compliance can impact supply chain vendors.
Even over the duration of a single year, rapid policy change and alterations to the direction of business objectives can create massive shifts in regulatory frameworks. For example, over the course of 2020, 55% of businesses changed their plans in relation to sustainable practices.
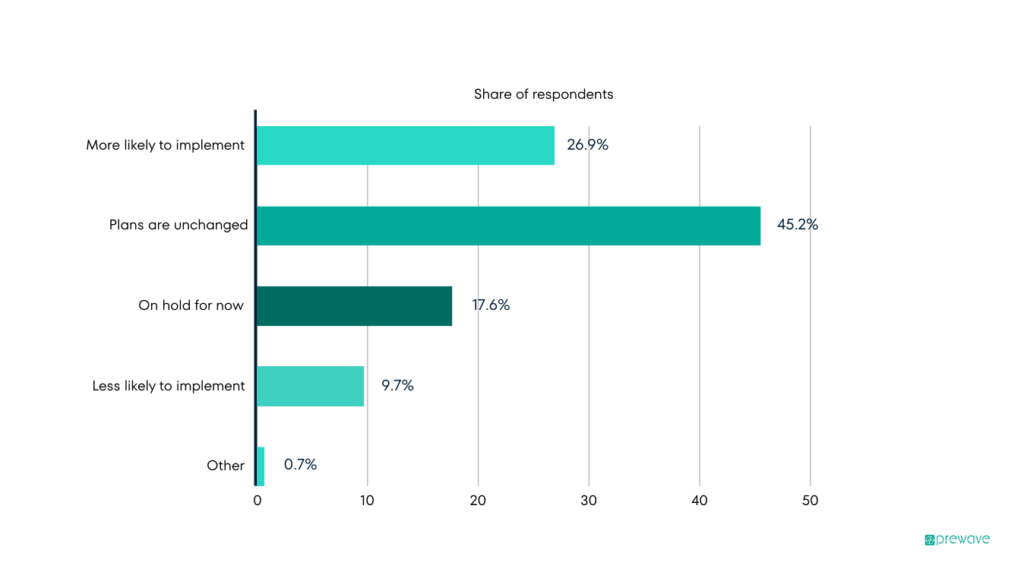
Source: Changes in plans to implement environmentally sustainable practices 2020.
In 2024, we’ve already seen discussions of the CSDDD, which will radially impact sustainability and human rights compliance objectives across the EU. While changing compliance does pose a potential issue, it’s also another aspect of procurement auditing that businesses can prepare for.
Regulatory change doesn’t come out overnight. In the case of the CSDDD, drafting and discussion periods lasted well over a year, with businesses still having several years of leeway before they must comply.
It’s vital that an organisation maintains a keen eye on future legislative changes and takes preemptive steps to ensure future compliance.
Remote Auditing and Virtual Compliance Inspections
Another major trend that’s shaping procurement audit procedures is the mass movement toward remote auditing. As businesses continue to expand across the globe, large distances between central business hubs and supplier networks make in-person auditing increasingly unfeasible.
Yet, while some may believe that remote auditing is less comprehensive, this is far from reality. Armed with a range of emerging tools, like AI, predictive analytics, blockchain logging, and more, audits are now equally as effective, no matter where they are conducted from.
Research from Informa suggests that the vast majority of audit staff do not perceive a shift in their ability to complete tasks when moving to remote auditing. Most responses report either no change when moving to remote auditing structures or a highly positive effect.
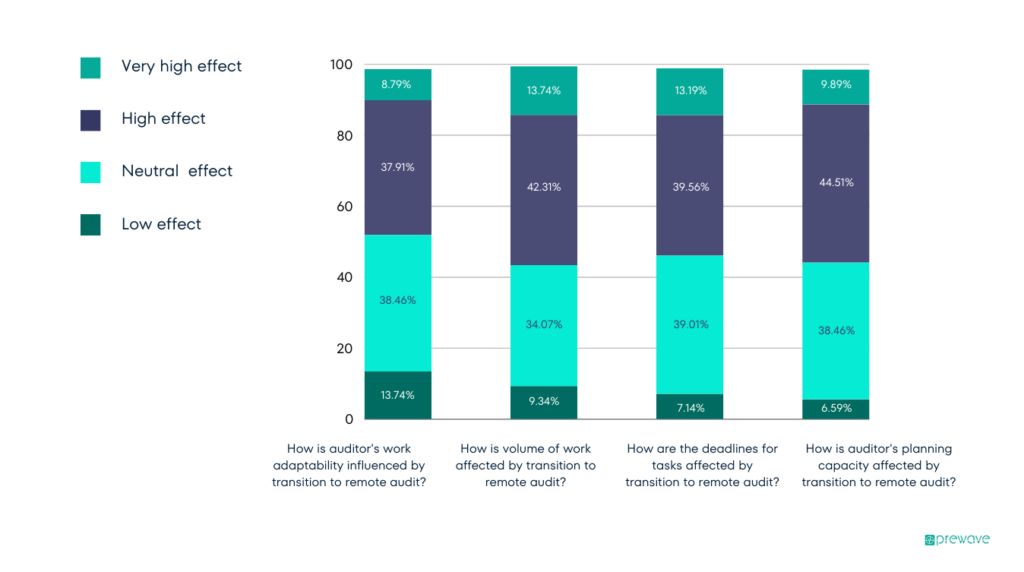
Source: Distribution of auditors’ perception on work adaptability/efficiency.
Businesses can resort to remote auditing to:
- Reduce Costs: Remote audits ensure that auditors don’t have to travel across countries or even continents to conduct a comprehensive review of practices. Remote auditing eliminates the need to fly to a business, dramatically reducing costs. At present, the vast majority, coming in at 82% of executives, are in favour of remote audits.
- Enhance Auditing Efficiency: Auditors can gather all relevant documents, frameworks, and procedure steps in one central location, giving them easy access to everything they need to conduct an audit via video call. With high-quality cameras, Wi-Fi connection, and virtual meeting platforms, they can conduct audits in a fraction of the time and avoid any potential disruptions caused by travel.
- Generate Consistent Audits: While audits must be carried out across certain periods, the ability to rapidly conduct a remote audit enhances the frequency with which businesses put their suppliers to the test. In procurement, businesses must be able to count on their suppliers, risking the integrity of their supply chain. By conducting regular audits remotely, they can be more confident in the longevity of suppliers.
Especially as businesses increasingly distribute their workforce and supply chain hubs across the globe, remote auditing is becoming a central trend in procurement auditing.
The Role of Sustainability in Procurement
Sustainability has become a major point of discussion in procurement auditing over the past two decades. The vast majority of fundamental changes to procedure and compliance frameworks have stemmed from Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) reporting shifts.
The increasing importance of sustainability reflects the potential disasters of climate change, with governments around the world developing compliance strategies to hold companies more accountable for their actions and processes. The supply chain, spanning across every major territory, is directly impacted by these policy changes.
Most recently, the introduction of the Corporate Sustainability Reporting Directive (CSRD) in January 2023 has forced businesses operating in the EU to enhance their ESG reporting efforts. While important, the CSRD is far from the only piece of legislation that will impact sustainability in the supply chain.
Here are a few central ways that ESG reporting will influence procurement:
- Environmental Reporting – Environmental shifts toward sustainable practices are potentially the site of the most extensive changes the procurement audit industry has seen over recent years. An increasing demand for clean energy consumption, effective waste management, offsetting carbon emissions, and the rising use of sustainable materials are all now essential for businesses to monitor. Some jurisdictions can find organisations liable if they do not audit the environmental reporting of their partners and subsidiaries.
- Social Reporting – Social policies, like fair trade, anti-modern slavery obligations, and the provision of fair working conditions, are increasingly monitored on an international scale. Businesses must investigate their suppliers, looking at potential breaches in the procurement chain of operations.
- Governance Metrics – Businesses must be aware of the potential obligations of each of the suppliers they work with. Audits should seek to explore the governmental relationships that their suppliers abide by, seeking out potential corruption, fraudulent practices, or failures in transparency.
Procurement auditing must increasingly scale to meet the emerging demands of each sector. As a primary consideration for almost every government across the globe, ESG reporting objectives are and will continue to be a central point of conversation going forward.
Final Thoughts: Embracing the Future of Procurement Audit and Compliance
The world of procurement auditing directly reflects the rapidly changing political and technological contexts of modern trade. As new regulatory frameworks come into force, this industry must always react – potentially using predictive and preemptive strategies to change policy ahead of time.
Equally, with the numerous emerging technologies like predictive analytics, blockchain, and risk management software, procurement auditing is at the forefront of digital transformation. Businesses can now conduct audits completely virtually, leveraging the plethora of digital technologies at their disposal to enhance auditing and improve transparency.
Prewave offers extensive risk management, prediction, and mitigation software. Businesses can streamline procurement audits with real-time assessments, proactively addressing risks before they escalate.
Incorporating Prewave into procurement audit strategies is a powerful way of staying on the cutting edge. With digital tools, emerging technologies, and proactive strategies, Prewave helps enhance and refine procurement audit and compliance. Get started today by booking a demo or reach out to the team for more information.




